Blood Pressure Monitors
The force of circulating blood on the walls of the arteries. Blood pressure is taken using two measurements: systolic (measured when the heart beats, when blood pressure is at its highest) and diastolic (measured between heart beats, when blood pressure is at its lowest). Blood pressure is written with the systolic blood pressure first, followed by the diastolic blood pressure
The only way to know if you have high blood pressure (HBP, or hypertension) is to have your blood pressure tested. Understanding your results is key to controlling high blood pressure.
Your blood pressure is recorded as two numbers:
- Systolic blood pressure (the first number) – indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls when the heart beats.
- Diastolic blood pressure (the second number) – indicates how much pressure your blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting between beats.
Normal Blood pressure numbers of less than 120/80 mm Hg are considered within the normal range. If your results fall into this category, stick with heart-healthy habits like following a balanced diet and getting regular exercise.
Elevated blood pressure is when readings consistently range from 120-129 systolic and less than 80 mm Hg diastolic. People with elevated blood pressure are likely to develop high blood pressure unless steps are taken to control the condition.
Hypertension Stage 1 is when blood pressure consistently ranges from 130-139 systolic or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic. At this stage of high blood pressure, doctors are likely to prescribe lifestyle changes and may consider adding blood pressure medication based on your risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), such as heart attack or stroke.
Hypertension Stage 2 is when blood pressure consistently ranges at 140/90 mm Hg or higher. At this stage of high blood pressure, doctors are likely to prescribe a combination of blood pressure medications and lifestyle changes.
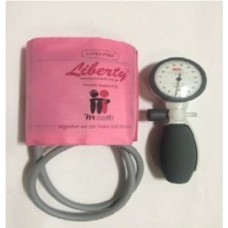
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer One-handed With Adult Cuff (Royal Blue) X1 Medical
..
$44.00 Ex Tax: $40.00
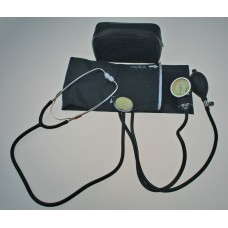
Blood Pressure Cuff & Bladder Set Royal Blue Adult Medical Device Latex Free
..
$33.00 Ex Tax: $30.00
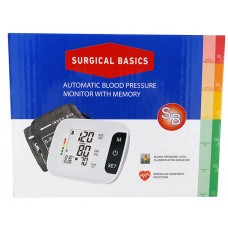
Blood Pressure Monitor Digital Automatic With Cuff Medical Equipment Device
..
$126.50 Ex Tax: $115.00
Large Adult Velcro Cuff Black Blood Pressure 62x18cm Medical Device Equipment
..
$16.50 Ex Tax: $15.00
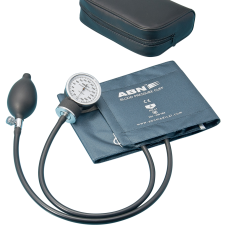
Sphygmomanometer Blood Pressure Kit Aneroid Abn Quality Grey Cuff Tga Approved
..
$55.00 Ex Tax: $50.00
Sphygmomanometer Palm Lite Handheld Aneroid Abn Quality Black Cuff Tga Approved
..
$121.00 Ex Tax: $110.00

 AUSTRALIA-WIDE SHIPPING $15
AUSTRALIA-WIDE SHIPPING $15